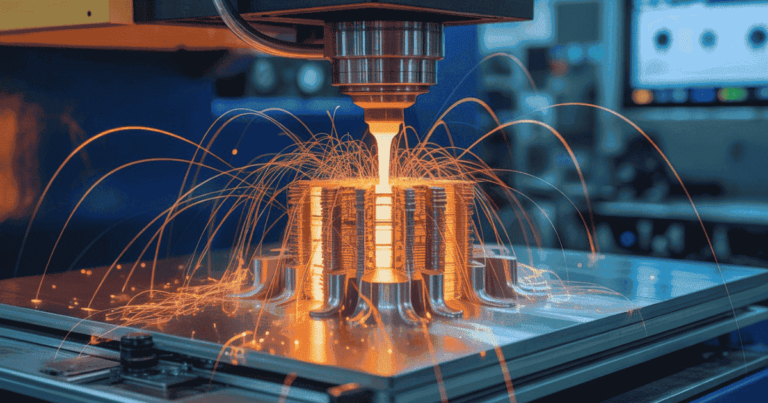
Metal 3D printing represents one of the greatest technologies in modern manufacturing, altering how industries design and produce their products. Rather than a more traditional cutting or casting approach, the technology builds the metal layer by layer with amazing precision. Many people want to know how does metal 3D printing work, and why is it being more widely adopted across diverse fields including aerospace, healthcare, and automotive. The process appears incredibly futuristic, yet it is being used by people and companies across the globe to create strong, complex, and custom parts.
This article will discuss the technical process, the benefits of metal 3D printing, and the several methods utilized. By the end of this article, you should have a relatively thorough understanding of how does metal 3D printing work and how it is shaping the future of manufacturing.
What Makes Metal 3D Printing Different?

Metal 3D printing is a different way of creating metal products, compared to traditional manufacturing. With traditional manufacturing, you start with a solid block of material that is machined to remove material and make a part. 3D printing builds up parts by adding layers of very fine metal powder (or wire) until you have a finished product.
3D printing reduces waste, allows for complex designs, and manufacturers lightweight yet strong structures in a single process. Industries that require precision, like medical implants or jet engine parts, take particular interest in 3D printing because it can produce customized shapes that would have been near impossible with previous technologies.
The Basic Steps in Metal 3D Printing
To learn about metal 3D printing, let’s look at the steps to see how it works:
Designing the Model – It all starts with a digital 3D design made in CAD software. This file is what the printer will use to print the object.
Preparing the Printer – The selected metal will typically be in either powder or wire form and then loaded into the machine.
Layer-by-Layer Printing – By using methods like laser melting or electron beams, the printer fuses the materials together layer by layer until the object is complete.
Cooling and Solidifying – Each layer is cooled and solidified before the next layer is added. Again, the goal is to maintain the strength of the structural material.
Post-Processing – After the printing is complete, the object may go through polishing, machining, or heating, among other post-processing work before being used to ensure that it is the correct shape, and size and that it is durable and aesthetically pleasing.
Common Techniques in Metal 3D Printing
There are a number of processes to consider, as it all depends on the part and the industry. Here are a few examples of commonly used processes:
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
SLM uses a high-powered laser to melt and melt the fine metal powders, layer by layer, to result in parts that are very accurate and made from strong, dense materials.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Using a laser, DMLS also melts the fine metal powder but slightly below the melting temperature to allow it to stick together vs melt. Ideal for parts with complex geometries.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Rather than using a laser, EBM uses an electron beam to melt the powder, and does this in a vacuum environment. EBM is used in applications such as aerospace and medical implants.
Binder Jetting
This process of 3D printing metal works by spraying a liquid binding agent over the layers of metal powder to bind them together. Once complete, the object is placed in a furnace to gain strength through sintering. Binder Jetting allows you to produce parts more quickly and is typically less expensive for larger size parts.
Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing can be seen as more than just a trend; it allows for practical benefits:
Complex designs – Engineers will be able to create shapes not possible using traditional manufacturing.
Material efficiency – Metal 3D printing uses less raw material due to only producing the necessary layers.
Customization – Metal 3D printing allows for custom designs, which is great for the healthcare industry when specific implants are required.
Durability – Metal 3D printing produces robust and reliable parts that can withstand extreme stress and heat.
Fast prototyping – Metal 3D printing uses to time from idea to part allowing for rapid innovation.
Industries Benefiting from Metal 3D Printing
Aerospace – Light-weight high-strength parts are important for aircraft and rockets.
Medical – Patient specific implants and surgical instruments.
Automotive – Prototyping and production for durable and high-performance automotive parts.
Energy – Turbine and engine parts that can withstand extreme temperatures and loads.
Challenges to Consider
Although powerful, metal 3D printing comes with challenges that industries must consider:
High Costs – Printer and raw materials can cost a lot of money.
Post-Processing Requirements – A lot of parts need post-processing after being printed.
Limitations in Materials – There are still certain metals that cannot be printed easily.
Technical Skills – Operators and engineers with a level of skill is required to get the best out of the process.
The Future of Metal 3D Printing
As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that costs will decrease and adoption will grow across different industries. Future advancements are likely to include even faster print speeds, greater material choices, and smarter printers that need less post-processing. With sustainability now a global objective, the material efficiency of metal 3D printing makes it appealing for sustainable production.
Conclusion
Metal 3D printing is not a thing of the future anymore; we are already starting to see how it changes industries across the globe. This technology, which builds parts from layers of material, has the potential to create products that minimize waste, maximize designs, and retain strength and reliability. When individuals ask how does metal 3D printing work, the answer is precision engineering, digital design, and material science.
From aerospace to health care, the possibilities for innovation are endless. As costs decrease and new techniques are introduced, we will see it become a standard practice in global manufacturing. Understanding how does metal 3D printing work can benefit industries and indicate how future products may be made, smarter, stronger, and more sustainable.